Different Factor Endowments Explain Differences in
In economic reasoning the simplest case for this distribution is the idea that countries will have different ratios of capital to labor. Efficiency of processes C.

Factor Endowment Definition Meaning In Stock Market With Example
The Heckscher Ohlin H - O theorem explains the reasons or.
. Differences in factor intensity in the production of different goods. Jump to navigation Jump to search. The Ricardian Classical model emphasized differences in technology.
The theory states that the differences in the costs of production stems from the differences in the supply of factor endowments. The FPP will be concave and not linear as in the Ricardian case. The intuition behind this case is that different factor endowments between countries are totally absorbed by different technologies rather than by different price ratios of final goods.
They explained that it is differences in factor endowments of different countries and different factor-proportions needed for producing different commodities that account for difference in comparative costs. The Heckscher-Ohlin model assumes two production factors and an internationally uniform production for each of two industries. Differences in relative scarcity of factors of production in different countries resulting into different factor prices.
The Heckscher-Ohlin theory predicts that countries will export those goods that make intensive use of factors that are locally abundant while importing goods that make intensive use of factors that. It lacks commonsense appeal. Countries relative endowments become more similar.
It is a basic model of trade and production. This paper considers whether it is differences in technical efficiency or differences in factor endowments that explain productivity differentials in Moldovan agriculture. Because we have two substitutable factors of production and not 1 with decreasing marginal productivity.
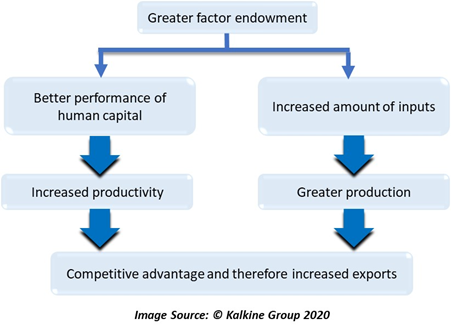
The following points highlight the nine main factors that cause differences in comparative advantage. Different factor endowments explain. There is widespread agreement that all these factors and many.
It emphasises the differences in factor endowment between countries are the basis for international trade. The model is a four-good version of the Davis 1995 Heckscher-Ohlin-Ricardo model of international trade based on technological and factor endowment differences across countries. A model is developed that can explain this phenomenon.
It is a relatively poor predictor of real-world international trade patterns. Nations have varying factor endowments and different factor endowments explain differences in factor costs. We assume constant returns to scale and free trade.
The Heckscher Ohlin theory is altogether different from the classical economists for two reasons. Y R Apv 1 Where Y is the value added A is the vector of total factor productivities p is the vector of. Different factor intensities or combinations are required for the production of various goods.
Industries can require different mixes of various inputs There is a systematic relationship between the factor endowments of a country and the winners and losers from trade. The more abundant a factor the lower its cost. Differences in factor endowments between countries.
Analyze the factors causing differences in the countries comparative advantage. Product Life Cycles 8. FACTOR ENDOWMENTS AND PER CAPITA INCOME DIFFERENCES AMONG COUNTRIES THE days when a single factor-capital skills entrepreneurship-was believed to be the key to economic development and hence the single explanatory variable in explaining income differences have long since passed.
Nations have varying factor endowments and different factor endowments explain differences in _____. Nations have varying factor endowments and different factor endowments explain differences in factor costs. Anything that produces different relative prices is a potential source of comparative advantage.
This new theory is therefore-called Heckscher-Ohlin theory of international trade. Vernons product life-cycle theory Vernons theory was based on the observation that for most of the twentieth century a very large proportion of the worlds new products had been developed by US. Heckscher-Ohlin HO theory is also known as factor-endowment theory.
Argues that the pattern of international trade is determined by differences in national factor endowments. Differences in endowments of factors of production is the focus of the Heckscher-Ohlin model. Factor endowment theory is used to determine comparative advantage.
We compute non-parametric measures of technical efficiency for a sample of Moldovan small-holders using the four-step Data Envelopment Analysis DEA approach suggested by Fried Schmidt and. These differences determine comparative advantage. Specifically the more abundant a factor the lower its cost.
It cannot be subjected to many empirical tests. According to Ohlin trade between nations is based on the fact that there are differences in factor endowments. In the second case that the two industries choose different factor intensities in equilibrium it is shown that the four theorems of the HO model are valid.
- 7929022 smirales8268 smirales8268 12252017 Biology High School answered expert verified Nations have varying factor endowments and different factor endowments explain differences in _____. Predicts that countries will export those goods that make intensive use of factors that are locally abundant while importing goods that make. Firms and sold first in the US.
It does not explain the differences in national factor endowments. Differences in their technologies andor factor endowments. Since there is wide agreement among modern economists about the explanation of.
The factor endowment theory holds that countries are likely to be abundant in different types of resources. The difference in autarky relative prices between countries. We start with the economy-wide revenue function.
The Hecksher-Ohlin theory of factor endowment in international trade is used to determine comparative advantage of various countries. It argues that comparative advantage arises from differences in the countries labor productivity. Factor costs Nations have varying factor endowments and different factor endowments explain differences in factor costs.
178 Nations have varying factor endowments and different factor endowments explain differences in _____.

Econ 333 Lesson 1 Quiz Answers Penn State University Lesson Penn State University Penn State

Factor Endowments And The Heckscher Ohlin Theory Economics Comparative Advantage Factors Of Production

Factor Endowment Definition Meaning In Stock Market With Example
Comments
Post a Comment